本节主要介绍sstable文件的格式及单个sstable文件的get/put。sstable文件全称是sorted string table,是一个有序且带索引的文件。
从前面的分析可知,level 0级的sstable文件是由内存中的immunable memtable经过minor compact形成的(也就是直接dump),而level>0级的文件是由level-1级别的文件经过major compact形成的。关于compact过程,我们在后续章节分析。这里着重于分析单个sstable文件的相关接口,代码在table/目录。
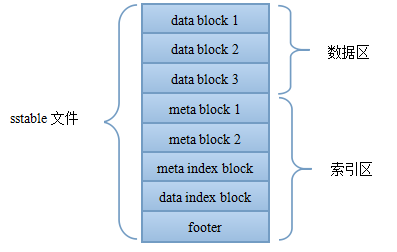
下图是sstable文件的整体结构。整体上,sstable文件分为数据区与索引区,尾部的footer指出了meta index block与data index block的偏移与大小,data index block指出了各data block的偏移与大小,meta index block指出了各meta block的偏移与大小。
先看footer结构。如下图。footer位于sstable文件尾部,占用空间固定为48个字节。其末尾8个字节是一个magic_number。metaindex_handle与index_handle物理上占用了40个字节,但实际上存储可能连32字节都不到。每一个handle的结构BlockHandle如右图,逻辑上分别表示offset+size,在内存中占用16个字节,但存储时由于采用可变长度编码,每个handle的物理存储通常不到8+8字节。因此这里两个handle总共占用不到32个字节,剩余填充0。
BlockHandle指出了block的偏移与大小。在sstable文件中,一般有多个data block,多个meta block(当前版本只有一个filter block,可扩充),1个meta index block,1个data index block。其中filter block的内部结构稍微不同于其他Block,但都是用BlockHandle来指向的。Footer与BlockHandle的代码主要format.cc/.h。其中Footer封装了footer的结构,BlockHandle对应图中的BlockHandle,另外有BlockContent表示从Block中实际读入的整个Block的字符串,而ReadBlock全局函数通过BlockHandle(指出了Block的偏移与大小)从指定文件中读取Block内容,并通过BlockContent返回。读取时可能需要校验crc32并解压。ReadBlock部分代码如下:
Status ReadBlock(RandomAccessFile* file,
const ReadOptions& options,
const BlockHandle& handle,
BlockContents* result) {
result->data = Slice();
result->cachable = false;
result->heap_allocated = false;
// Read the block contents as well as the type/crc footer.
// See table_builder.cc for the code that built this structure.
size_t n = static_cast<size_t>(handle.size());
char* buf = new char[n + kBlockTrailerSize];
Slice contents;
Status s = file->Read(handle.offset(), n + kBlockTrailerSize, &contents, buf);
if (!s.ok()) {
delete[] buf;
return s;
}
if (contents.size() != n + kBlockTrailerSize) {
delete[] buf;
return Status::Corruption("truncated block read");
}
// Check the crc of the type and the block contents
const char* data = contents.data(); // Pointer to where Read put the data
// crc32校验
if (options.verify_checksums) {
const uint32_t crc = crc32c::Unmask(DecodeFixed32(data + n + 1));
// data + type + crc
const uint32_t actual = crc32c::Value(data, n + 1);
if (actual != crc) {
delete[] buf;
s = Status::Corruption("block checksum mismatch");
return s;
}
}
switch (data[n]) {
case kNoCompression:
---
// Ok
break;
// snappy压缩
case kSnappyCompression: {
size_t ulength = 0;
if (!port::Snappy_GetUncompressedLength(data, n, &ulength)) {
delete[] buf;
return Status::Corruption("corrupted compressed block contents");
}
char* ubuf = new char[ulength];
if (!port::Snappy_Uncompress(data, n, ubuf)) {
delete[] buf;
delete[] ubuf;
return Status::Corruption("corrupted compressed block contents");
}
delete[] buf;
result->data = Slice(ubuf, ulength);
result->heap_allocated = true;
result->cachable = true;
break;
}
default:
---
}
---
}
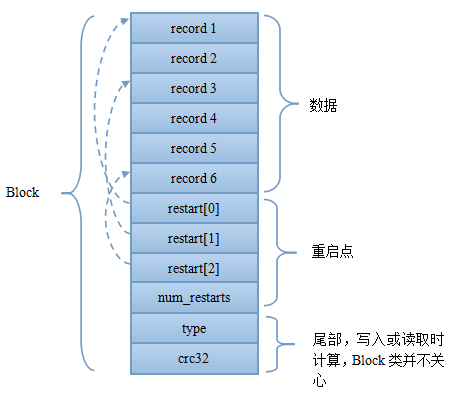
前面通过ReadBlock读取的BlockContent内容一般通过new Block(BlockContent)初始化为具体的Block对象。现在我们看看Block的内部结构,如下图。逻辑上主要分为数据与重启点。重启点也是一个指针,指出了一些特殊的位置。data block中的key是有序存储的,相邻的key之间可能有重复,因此存储时采用前缀压缩,后一个key只存储与前一个key不同的部分。那些重启点指出的位置就表示该key不按前缀压缩,而是完整存储该key。除了减少压缩空间之外,重启点的第二个作用就是加速读取。如果说data index block可以通过二分来定位具体的block,那么重启点则可以通过二分的方法来定位具体的重启点位置,进一步减少了需要读取的数据。对于leveldb来讲,可以通过options.block_size与options.block_restart_interval来设置block的大小与重启点的间隔。默认data block的大小为4K。而重启点则每隔16个key。具体的单条record的存储格式如下图所示。
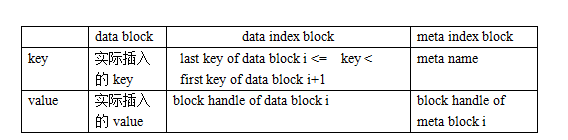
在进一步分析Block代码之前,我们先来搞清楚这样一个问题。前面提到,data block与meta index block、data index block都是采用block来存储的(filter block稍微不同)。而对于block来讲,其都是按(key,value)格式存储一条条的record的。对于这些不同类型的block,其(key,value)都是什么了?总结如下图。现在只有一个meta block用于filter,因此meta index block中也只有一条记录,其key是filter. + filter_policy的name。
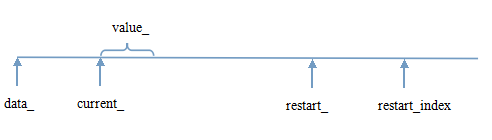
block的具体实现在block.cc/.h与block_builder.cc/.h中。前者用于读,后者用于写。读取时,一般先通过前面提到的ReadBlock读取一块至BlockContent中,然后再通过Block的构造函数初始化,并通过Block::Iter子类用于外部遍历或者定位具体某个key。Block类代码简单。Block::Iter的代码内部结构如下图所示。data_指向读入的BlockContent内容,current_指向当前的value,restart_则指出了重启点数据的起始位置,restart_index则对应当前value的重启点索引。查找时,先通过restart_index指向的value定位,找到相应的重启点后,再在重启点内部遍历。顺序遍历整个block时,需要注意修改restart_index_。代码细节请自行阅读。
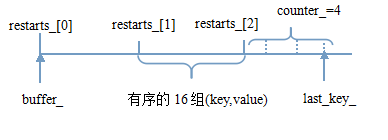
写block,则通过block_builder.cc/.h中的BlockBuilder类来完成。一般是通过多次调用Add方法,再Finish结束这个block。BlockBuilder的内部结构如下图。由于block的重启点位于block尾部,因此需要先保存这些重启点,Finish时再顺序写入。图中的restarts_ vector就是用来保存各个重启点偏移的。counter_用于计数,当超过重启间隔时,需开启一个新的重启点。最后Finish时顺序写入这些重启点。代码也很简单。
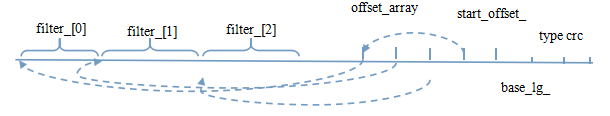
现在我们再来看看稍微特殊的FilterBlock。FilterBlock内部不像Block有复杂的(key,value)格式,其只有一个字符串。该字符串的内部结构如下图。filterblock保存多个filter string,每个filter string针对一段block,间隔为2^base_lg_,保存在末尾,默认值为2KB,也就是说,filter block每隔2kb block offset的key生成一个filter string,offset_array_指出了这些filter string的偏移。过滤时,一般先通过data index block获取key的大致block offset,再通过filter string的offset_array_获取该block offset的filter string,再进行过滤。生成时,对同一个block offset范围的数据一起构建filter string。具体代码细节在filter_block.cc/.h中。读写分别用FilterBlockReader与FilterBlockBuilder来封装。
最后我们来看看table类。table类表示了整个sstable文件。外部通过这个类访问sstable,table内部访问block/meta block。
外部使用时,主要有两类接口。一类是读,另一类是写。读接口在table.cc/.h中实现,写接口在table_builder.cc/.h中实现。读接口的调用顺序为,Open打开一个sst文件,然后NewIterator返回一个迭代器用于遍历整个table,或者调用InternalGet用于Seek某个key。这些接口一般通过table_cache类来调用。table_cache是table的缓存。table_cache会先查看是否有cache,没有则读table文件,写cache。table_cache的具体细节我们在Get章节中分析。写接口的调用顺序为,TableBuilder构造函数初始化–>多次调用Add(key,value)–>Finish/Abandon(异常退出)结束。InternalGet的主要代码如下。内部会先查询filter与BlockCache。
Status Table::InternalGet(const ReadOptions& options, const Slice& k,
void* arg,
void (*saver)(void*, const Slice&, const Slice&)) {
Status s;
Iterator* iiter = rep_->index_block->NewIterator(rep_->options.comparator);
//先定位该值的offset
iiter->Seek(k);
if (iiter->Valid()) {
Slice handle_value = iiter->value();
FilterBlockReader* filter = rep_->filter;
BlockHandle handle;
// 根据该offset查询filter
if (filter != NULL &&
handle.DecodeFrom(&handle_value).ok() &&
!filter->KeyMayMatch(handle.offset(), k)) {
// Not found
} else {
Slice handle = iiter->value();
// 没被过滤,表示该key可能存在,需要读取对应的block
Iterator* block_iter = BlockReader(this, options, iiter->value());
block_iter->Seek(k);
if (block_iter->Valid()) {
(*saver)(arg, block_iter->key(), block_iter->value());
}
s = block_iter->status();
delete block_iter;
}
}
---
}
Iterator* Table::BlockReader(void* arg,
const ReadOptions& options,
const Slice& index_value) {
Table* table = reinterpret_cast<Table*>(arg);
Cache* block_cache = table->rep_->options.block_cache;
Block* block = NULL;
Cache::Handle* cache_handle = NULL;
BlockHandle handle;
Slice input = index_value;
Status s = handle.DecodeFrom(&input);
// We intentionally allow extra stuff in index_value so that we
// can add more features in the future.
// block:先查block cache
// cache的key是table的cache_id + block_offset
// 每个table文件对应一个唯一的cache_id
if (s.ok()) {
BlockContents contents;
if (block_cache != NULL) {
char cache_key_buffer[16];
EncodeFixed64(cache_key_buffer, table->rep_->cache_id);
EncodeFixed64(cache_key_buffer+8, handle.offset());
Slice key(cache_key_buffer, sizeof(cache_key_buffer));
cache_handle = block_cache->Lookup(key);
if (cache_handle != NULL) {
block = reinterpret_cast<Block*>(block_cache->Value(cache_handle));
} else {
// 没有则直接读取,并加入block cache
s = ReadBlock(table->rep_->file, options, handle, &contents);
if (s.ok()) {
block = new Block(contents);
if (contents.cachable && options.fill_cache) {
cache_handle = block_cache->Insert(
key, block, block->size(), &DeleteCachedBlock);
}
}
}
} else {
s = ReadBlock(table->rep_->file, options, handle, &contents);
if (s.ok()) {
block = new Block(contents);
}
}
}
---
}
写table的主要函数Add与Finish代码如下。代码清晰,请自行阅读。
void TableBuilder::Add(const Slice& key, const Slice& value) {
Rep* r = rep_;
assert(!r->closed);
if (!ok()) return;
// 需要有序插入
if (r->num_entries > 0) {
assert(r->options.comparator->Compare(key, Slice(r->last_key)) > 0);
}
// 前面提到过data index block的key,其值需要等候后一个block的key写入时才能构造,pending_index_entry就表示了前一个block的index,此时构造其key,并写入index_block
if (r->pending_index_entry) {
assert(r->data_block.empty());
r->options.comparator->FindShortestSeparator(&r->last_key, key);
std::string handle_encoding;
r->pending_handle.EncodeTo(&handle_encoding);
r->index_block.Add(r->last_key, Slice(handle_encoding));
r->pending_index_entry = false;
}
// 往filter block中添加key
if (r->filter_block != NULL) {
r->filter_block->AddKey(key);
}
r->last_key.assign(key.data(), key.size());
r->num_entries++;
r->data_block.Add(key, value);
const size_t estimated_block_size = r->data_block.CurrentSizeEstimate();
// block_size限制
if (estimated_block_size >= r->options.block_size) {
Flush();
}
}
Status TableBuilder::Finish() {
Rep* r = rep_;
Flush();
assert(!r->closed);
r->closed = true;
BlockHandle filter_block_handle, metaindex_block_handle, index_block_handle;
// Write filter block
if (ok() && r->filter_block != NULL) {
WriteRawBlock(r->filter_block->Finish(), kNoCompression,
&filter_block_handle);
}
// Write metaindex block
if (ok()) {
BlockBuilder meta_index_block(&r->options);
if (r->filter_block != NULL) {
// Add mapping from "filter.Name" to location of filter data
std::string key = "filter.";
key.append(r->options.filter_policy->Name());
std::string handle_encoding;
filter_block_handle.EncodeTo(&handle_encoding);
meta_index_block.Add(key, handle_encoding);
}
// TODO(postrelease): Add stats and other meta blocks
WriteBlock(&meta_index_block, &metaindex_block_handle);
}
// Write index block
if (ok()) {
if (r->pending_index_entry) {
r->options.comparator->FindShortSuccessor(&r->last_key);
std::string handle_encoding;
r->pending_handle.EncodeTo(&handle_encoding);
r->index_block.Add(r->last_key, Slice(handle_encoding));
r->pending_index_entry = false;
}
WriteBlock(&r->index_block, &index_block_handle);
}
// Write footer
if (ok()) {
Footer footer;
footer.set_metaindex_handle(metaindex_block_handle);
footer.set_index_handle(index_block_handle);
std::string footer_encoding;
footer.EncodeTo(&footer_encoding);
r->status = r->file->Append(footer_encoding);
if (r->status.ok()) {
r->offset += footer_encoding.size();
}
}
return r->status;
}
另外还有two_level_iterator.cc/.h与merger.cc/.h类。前者用于构造table上的迭代器,后者用于多个迭代器的归并。