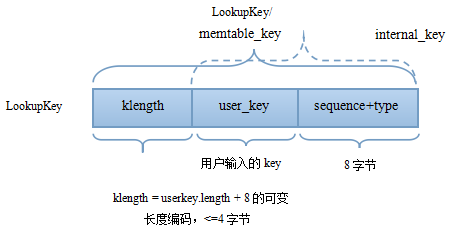
作为一个kv的系统,key的存储至关重要。在leveldb中,主要涉及到如下几个key,user_key、InternalKey与LookupKey(memtable_key)。
其关系构成如下图。user_key就是用户输入的key,而InternalKey在user_key的基础上封装了sequence_num+type。sequence_num是一个全局递增的序列号,每一次Put操作都会递增。这样,不同时间的写入操作会得到不一样的sequence_num。前面章节中提到的sstable单条record中的key,其内部其实就是一个InternalKey。sequence_num主要跟snapshot机制与version机制相关,对压缩会产生一定影响。这些我们在后续章节分析。根据type字段,可以获知本次写入操作是写还是删除(也就是说删除是一种特殊的写)。而LookupKey/memtable_key用于在memtable中,多了一个长度字段。代码主要在dbformat.cc/.h中。
static uint64_t PackSequenceAndType(uint64_t seq, ValueType t) {
assert(seq <= kMaxSequenceNumber);
assert(t <= kValueTypeForSeek);
return (seq << \8) | t;
}
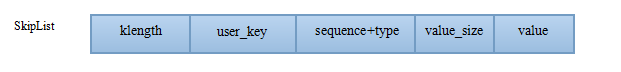
skiplist中的单个节点不仅存储了Key,也存储了value。格式如下图。尽管单个节点的开头部分是一个LookupKey,但其内部比较时,还是使用的InternalKey。也就是说,比较时,先使用InternalKey内部的user_key进行比较,再比较sequence_num。这样不管是memtable还是sstable文件,其内部都是按InternalKey有序的。
int InternalKeyComparator::Compare(const Slice& akey, const Slice& bkey) const {
// Order by:
// increasing user key (according to user-supplied comparator)
// decreasing sequence number
// decreasing type (though sequence# should be enough to disambiguate)
int r = user_comparator_->Compare(ExtractUserKey(akey), ExtractUserKey(bkey));
if (r == 0) {
const uint64_t anum = DecodeFixed64(akey.data() + akey.size() - 8);
const uint64_t bnum = DecodeFixed64(bkey.data() + bkey.size() - 8);
if (anum > bnum) {
r = -1;
} else if (anum < bnum) {
r = +1;
}
}
return r;
}
在进行Get操作时,leveldb会使用用户传入的user_key与当前db最大的sequence_num进行合并,以得到LookupKey(实际还会受snapshot机制影响)。但在内部查找时还是使用的InternalKey。
Put操作会稍微复杂点。leveldb的3种写入操作最终都会封装成WriteBatch。这3种写入操作分别是Put(写入单条key
/value)、Delete(删除单条key)、Write(批量进行Put与Delete操作)。WriteBath的内部格式如下图。WriteBatch所表示的多条记录最终会按SkipList所要求的格式1条条地顺序插入到memtable中。
Status WriteBatchInternal::InsertInto(const WriteBatch* b,
MemTable* memtable) {
MemTableInserter inserter;
// memtable 的初始sequence为WriteBatchInternal中的seq
inserter.sequence_ = WriteBatchInternal::Sequence(b);
inserter.mem_ = memtable;
return b->Iterate(&inserter);
}
Status WriteBatch::Iterate(Handler* handler) const {
Slice input(rep_);
if (input.size() < kHeader) {
return Status::Corruption("malformed WriteBatch (too small)");
}
// kHeader=12 = seq(8字节) + count(4字节)
input.remove_prefix(kHeader);
Slice key, value;
int found = 0;
while (!input.empty()) {
found++;
char tag = input[0];
// type:1字节
input.remove_prefix(1);
switch (tag) {
case kTypeValue:
if (GetLengthPrefixedSlice(&input, &key) &&
GetLengthPrefixedSlice(&input, &value)) {
handler->Put(key, value);
} else {
return Status::Corruption("bad WriteBatch Put");
}
break;
case kTypeDeletion:
if (GetLengthPrefixedSlice(&input, &key)) {
handler->Delete(key);
} else {
return Status::Corruption("bad WriteBatch Delete");
}
break;
default:
return Status::Corruption("unknown WriteBatch tag");
}
}
if (found != WriteBatchInternal::Count(this)) {
return Status::Corruption("WriteBatch has wrong count");
} else {
return Status::OK();
}
}
关于读写压缩等对key/value的具体操作,我们在后续章节进行分析,这里只需要了解大概。